Birth control isn’t just about avoiding pregnancy. It’s about owning your reproductive health. In today’s world, with so many contraceptive choices available, selecting the right one can feel overwhelming.
Whether you’re planning your future or managing a medical condition like PCOS or endometriosis, knowing the best birth control options in USA empowers you to make informed, personalized choices. This guide is designed to give you everything you need: from effectiveness and biological impact to side effects, costs, and ease of use.
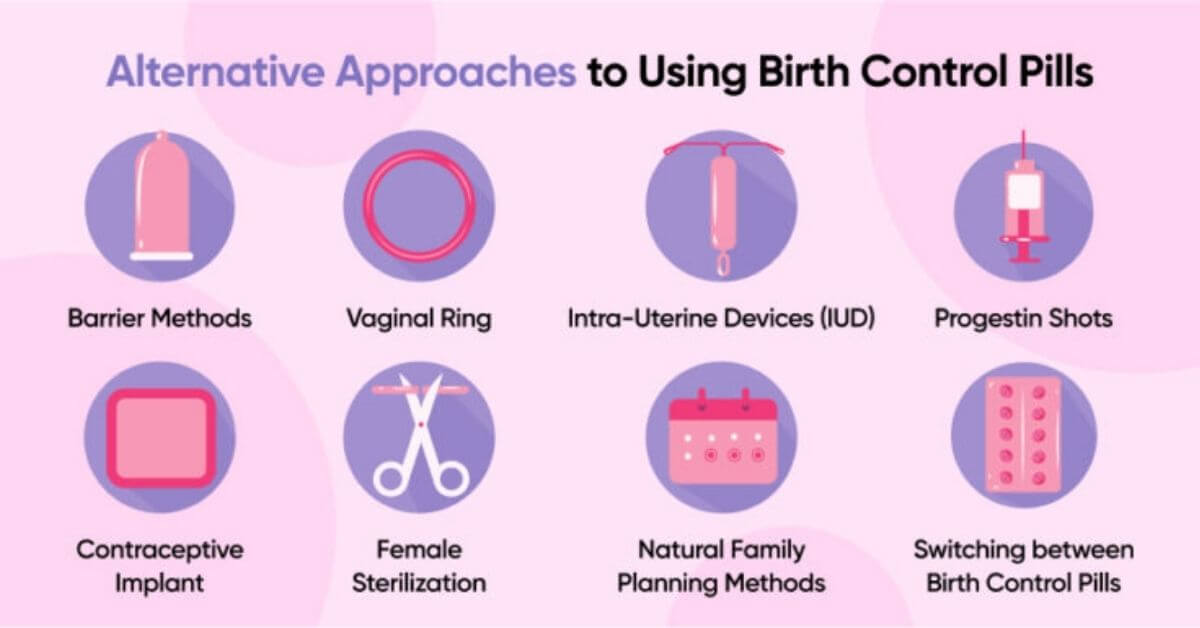
Understanding the Different Types of Birth Control
Choosing the right birth control method can feel like navigating a maze especially when the options range from daily pills to long-lasting implants and hormone-free solutions. In the USA, women and couples have access to a wide variety of safe and effective contraceptives. But with choice comes complexity.
To simplify things, birth control methods are grouped into several categories based on how they work, their duration, and whether they use hormones. Here’s a clear breakdown:
1. Hormonal Birth Control
These methods use synthetic hormones either estrogen, progestin, or both to prevent ovulation, thin the uterine lining, and thicken cervical mucus, making it harder for sperm to reach an egg.
Examples include:
- Birth control pills (daily oral contraceptives)
- The patch (a weekly skin patch)
- Vaginal ring (monthly insert)
- Birth control shot (Depo-Provera, given every 3 months)
Best for: Women who want short-term control and are okay with hormonal methods.
2. Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARCs)
LARCs are low-maintenance options that offer extended protection ranging from 3 to 10 years without requiring daily or weekly attention.
Includes:
- Hormonal IUDs (like Mirena, Skyla, Liletta, Kyleena)
- Non-hormonal IUD (Paragard, copper-based)
- Birth control implant (Nexplanon, inserted under the skin of the upper arm)
Best for: People seeking high effectiveness with minimal effort.
3. Non-Hormonal Birth Control
Not everyone wants to use hormones. Non-hormonal methods either act as physical barriers or depend on awareness of your body’s natural fertility cycle.
Common types:
- Copper IUD (no hormones, toxic to sperm)
- Condoms (male and female, also protect against STIs)
- Diaphragm or cervical cap (covers cervix to block sperm)
- Sponge (spermicide-filled device placed in the vagina)
- Fertility Awareness Methods (FAMs) (tracking ovulation and avoiding sex on fertile days)
Best for: Those with hormone sensitivity or who prefer natural methods.
4. Emergency Contraception
Designed for use after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure, emergency contraception is a backup not a primary method.
Options:
- Morning-after pills like Plan B or Ella
- Copper IUD (if inserted within 5 days)
Best for: Unplanned situations needing quick action.
5. Permanent Birth Control
When you’re absolutely sure you don’t want children in the future, permanent methods provide lifelong protection.
Includes:
- Female sterilization (tubal ligation or tubal removal)
- Male vasectomy (cutting sperm ducts)
Best for: Individuals or couples done with childbearing.
PCOD Food Chart: A Balanced Diet Plan for Hormonal Harmony & Weight Management
Hormonal Birth Control Options
Hormonal birth control methods are among the most widely used contraceptives in the USA. They work by changing the body’s natural hormone levels primarily estrogen and progestin to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin the uterine lining. These changes make it extremely difficult for sperm to fertilize an egg or for a fertilized egg to implant.
Women across the United States often prefer hormonal options because they offer added benefits beyond pregnancy prevention, such as regulating menstrual cycles, improving acne, and easing the symptoms of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis.
Let’s explore the most popular and medically approved hormonal birth control options in USA:
1. Birth Control Pills
What they are:
Oral contraceptive pills are taken once daily, usually at the same time each day. There are two types:
- Combination pills: Contain both estrogen and progestin
- Progestin-only pills (Mini-pills): Ideal for women sensitive to estrogen or breastfeeding mothers
How they work biologically:
These pills prevent the release of an egg (ovulation). They also change the cervical mucus, making it hard for sperm to travel, and alter the uterine lining to reduce implantation chances.
Effectiveness:
- About 91% effective with typical use
- Over 99% effective with perfect use
Pros:
✔ Highly effective when used correctly
✔ Helps regulate periods
✔ Can improve skin conditions like acne
✔ Reduces menstrual cramps and ovarian cyst risk
Cons:
✘ Must be taken at the same time every day
✘ May cause nausea, breast tenderness, mood swings
✘ Slightly increases the risk of blood clots (especially in smokers over 35)
Best for: Women who prefer routine and are comfortable taking a daily pill.
2. Birth Control Patch
What it is:
A thin, beige patch that sticks to your skin usually on your arm, back, buttocks, or abdomen.
How it works:
Releases estrogen and progestin through the skin into the bloodstream. It stops ovulation and thickens cervical mucus, similar to the pill.
Usage:
- Worn for one week, changed weekly for three weeks, then removed for one week off (to allow a period)
Effectiveness:
- 91% effective with typical use
Pros:
✔ Convenient weekly schedule
✔ Steady hormone delivery
✔ Regulates periods
Cons:
✘ May cause skin irritation
✘ Visibility could be a concern for some
✘ Less effective for women weighing over 198 pounds
Best for: Women who want a “set-it-and-forget-it” option without taking a daily pill.

3. Vaginal Ring (NuvaRing or Annovera)
What it is:
A small, flexible plastic ring inserted into the vagina. It stays in place for several weeks and releases low doses of estrogen and progestin.
How it works:
It prevents ovulation and thickens cervical mucus. Hormones are absorbed locally but have system-wide effects.
Usage:
- NuvaRing: Insert for 3 weeks, remove for 1 week
- Annovera: Reusable for up to 1 year
Effectiveness:
- 91% effective with typical use
Pros:
✔ Monthly maintenance
✔ Discreet and comfortable for most users
✔ Less hormonal fluctuation than pills
Cons:
✘ May cause vaginal irritation
✘ Needs to be inserted and removed correctly
✘ Not suitable for women sensitive to estrogen
Best for: Women looking for a low-effort, long-term method without daily management.
Reclaiming Your Strength: Comprehensive Postpartum Workout Plans for Every Mom
4. Birth Control Shot (Depo-Provera)
What it is:
An injectable form of progestin-only contraception, given every three months by a healthcare provider.
How it works:
The shot suppresses ovulation, thickens cervical mucus, and thins the uterine lining.
Effectiveness:
- 94% effective with typical use
- Over 99% with timely injections
Pros:
✔ Only 4 times a year
✔ Can stop periods over time
✔ Effective within 24 hours after injection
Cons:
✘ Irregular bleeding initially
✘ Delayed return to fertility (can take 9-12 months)
✘ Potential for bone density loss with long-term use
✘ Possible weight gain
Best for: Women seeking a private, long-term method without daily or weekly commitment.
Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARCs)
If you’re looking for the most convenient and low-maintenance birth control solutions available in the USA, Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARCs) may be your perfect match.
These methods offer years of protection from pregnancy without requiring daily or monthly attention. Once in place, you can forget about them and still enjoy peace of mind. That’s why LARCs are considered among the best birth control options in USA by OB-GYNs, healthcare organizations, and patients alike.
Unlike pills or patches, LARCs don’t rely on perfect usage to be highly effective. The chances of human error are nearly eliminated, making them ideal for busy professionals, students, new moms, and anyone who wants consistent, reliable contraception.
Let’s explore the two primary types of LARCs: IUDs and the birth control implant.
1. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device that a healthcare provider inserts into your uterus. It’s designed to prevent pregnancy for several years and can be removed at any time if your plans change.
There are two types of IUDs used in the USA: Hormonal IUDs and the Non-Hormonal Copper IUD (covered in the next section). Here, we’ll focus on the hormonal ones.
Hormonal IUDs (Mirena, Kyleena, Skyla, Liletta)
How they work biologically:
These IUDs release a small, steady dose of progestin (levonorgestrel) into the uterus. This hormone thickens cervical mucus to block sperm, thins the uterine lining to prevent implantation, and in some women, suppresses ovulation.
Duration and Effectiveness:
- Mirena: Up to 8 years
- Kyleena: Up to 5 years
- Skyla: Up to 3 years
- Liletta: Up to 8 years
- Effectiveness: Over 99%, making them as reliable as sterilization
Best for: Women seeking highly effective, long-term birth control without the hassle of daily or monthly tasks.
2. Birth Control Implant (Nexplanon)
Nexplanon is a tiny, flexible rod about the size of a matchstick inserted under the skin of your upper arm by a healthcare provider.
How it works biologically:
The implant continuously releases progestin, preventing ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and altering the uterine lining.
Duration and Effectiveness:
- Protects against pregnancy for up to 3 years
- More than 99% effective comparable to IUDs and sterilization
Best for: Women wanting the most discreet and effective birth control with minimal effort.
Non-Hormonal Birth Control Options
Not everyone wants or can tolerate hormonal contraception. Some women experience side effects like mood swings, nausea, or headaches when using hormones. Others simply prefer a more natural, hormone-free lifestyle. Fortunately, there are safe, effective, and medically approved non-hormonal birth control options in USA that offer flexibility and peace of mind.
Non-hormonal birth control works by either physically blocking sperm from reaching the egg or by using substances or techniques to prevent fertilization. These methods don’t interfere with your natural hormone levels, making them a popular choice for those with health concerns or personal preferences.
Let’s explore your top hormone-free options.
1. Copper IUD (Paragard)
What it is:
Paragard is the only non-hormonal intrauterine device (IUD) currently available in the USA. It’s a small T-shaped device wrapped in copper wire, inserted by a healthcare provider into the uterus.
How it works biologically:
Copper is toxic to sperm. It creates an inflammatory reaction in the uterus that prevents sperm from reaching and fertilizing the egg. It does not interfere with ovulation.
Effectiveness:
- Over 99% effective
- Provides protection for up to 10 years
Best for: Women who want long-term, maintenance-free contraception without hormones.
2. Barrier Methods
Barrier methods physically block sperm from entering the uterus. These are available over the counter and can be used on demand.
A. Male Condoms
How it works:
Covers the penis during sex, preventing semen from entering the vagina.
Effectiveness:
- 85% effective with typical use
- Protects against STIs (sexually transmitted infections)
Best for: Anyone wanting dual protection (pregnancy + STI prevention).
B. Female Condoms
How it works:
Inserted into the vagina before intercourse to create a barrier against sperm.
Effectiveness:
- Around 79% effective with typical use
C. Diaphragm and Cervical Cap
These are reusable, dome-shaped silicone devices placed inside the vagina to cover the cervix and prevent sperm entry. Must be used with spermicide to be effective.
Effectiveness:
- Diaphragm: 88%
- Cervical Cap: 71–86% depending on birth history
Best for: Women looking for non-daily, reusable barrier contraception without hormones.
D. Contraceptive Sponge
A soft, disk-shaped sponge saturated with spermicide, inserted into the vagina before sex.
Effectiveness:
- 76–88% depending on prior pregnancies
3. Fertility Awareness-Based Methods (FAMs)
FAMs involve tracking your menstrual cycle, body temperature, and cervical mucus to identify your fertile days and avoiding sex (or using protection) during that time.
Types include:
- Calendar Method
- Basal Body Temperature Tracking
- Cervical Mucus Monitoring
- Fertility Apps (e.g., Natural Cycles)
Effectiveness:
- 76–88% effective with typical use
- Up to 95–99% effective with perfect use
Best for: Highly motivated and organized individuals with regular cycles.
4. Spermicide
A chemical that kills sperm, used alone or with barrier methods like condoms or diaphragms.
Effectiveness:
- Around 71–82% when used alone
Forms available:
Gels, foams, films, suppositories
Best for: Occasional use or as a backup with other barrier methods.
Permanent Birth Control Options
Sometimes, birth control isn’t just about “for now” it’s about forever. When you’re absolutely certain you don’t want children in the future (or you’re done growing your family), permanent birth control options in USA offer reliable, hormone-free, and one-time solutions with minimal maintenance.
These methods are also called sterilization procedures, and they are designed to be irreversible. That’s why making an informed, confident decision backed by medical advice is crucial before moving forward.
What Is Permanent Birth Control?
Permanent contraception prevents pregnancy for life. It involves surgical or non-surgical methods that either block or cut the reproductive pathways sperm ducts in men or fallopian tubes in women.
Two primary types:
- Female sterilization – Tubal ligation or tubal removal
- Male sterilization – Vasectomy
Let’s explore how each works biologically and practically.
1. Female Sterilization (Tubal Ligation or Salpingectomy)
Often referred to as “getting your tubes tied,” this procedure is one of the most common permanent birth control options for women in the USA.
How It Works Biologically:
- The fallopian tubes are either cut, sealed, tied, clipped, or completely removed.
- This blocks the path between the ovary and uterus, so eggs can’t meet sperm.
- Ovulation still occurs, and menstrual cycles continue as normal.
- The procedure does not affect hormone levels or sex drive.
Effectiveness:
- Over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy.
- Failure rate is less than 1 in 200.
Types of Procedures:
- Tubal Ligation (traditional method): The tubes are tied, cut, or sealed.
- Bilateral Salpingectomy: The entire fallopian tubes are removed. Recent research shows this may lower ovarian cancer risk.
- Laparoscopic Surgery (minimally invasive): Performed under general anesthesia with small abdominal incisions.
Best For:
Women who are done having children or are 100% certain they don’t want any. It’s also a great fit for those seeking hormone-free birth control for life.
2. Male Sterilization (Vasectomy)
Though often overlooked, vasectomy is safer, simpler, and more cost-effective than female sterilization. It’s one of the most reliable birth control options in USA for men who are done having children.
How It Works Biologically:
- The vas deferens the tubes carrying sperm from the testicles are cut and sealed.
- This prevents sperm from mixing with semen during ejaculation.
- The body still produces sperm, but they are reabsorbed harmlessly.
Effectiveness:
- Over 99.85% effective more reliable than any other form of birth control.
Procedure Details:
- Outpatient, done in 20–30 minutes
- Local anesthesia
- Minimal discomfort
- Recovery within 2–3 days
Best For:
Men who are completely certain about not having (or having more) children and want a one-time, maintenance-free birth control method.
Birth Control for Special Health Conditions
Choosing the right contraceptive isn’t one-size-fits-all especially when you’re managing specific health conditions. If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, migraines, PCOS, obesity, blood clot risks, or other chronic illnesses, birth control options must be tailored carefully to protect your health and your reproductive goals.
Fortunately, modern medicine offers several safe and effective birth control options in USA that can be adapted to your medical needs.
Why Special Consideration Matters
Certain birth control methods especially hormonal options can interact negatively with existing health issues, increasing your risk for complications such as:
- Blood clots
- Stroke
- Heart disease
- Elevated blood pressure
- Hormonal imbalance
That’s why understanding the science behind how birth control affects your condition is key to making a safe and smart choice.
1. Birth Control for Women with Hypertension
High blood pressure can be made worse by estrogen-containing birth control like the combined pill, patch, or vaginal ring.
Safe Choices:
- Progestin-only pills (Mini Pill)
- Hormonal IUDs (e.g., Mirena)
- Implant (Nexplanon)
- Copper IUD (Paragard)
- Barrier methods (condoms, diaphragms)
Avoid: Estrogen-based contraceptives, as they may increase blood pressure or risk of stroke, especially if you’re over 35 or a smoker.
2. Birth Control for Diabetics
Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes must watch for hormonal fluctuations that could impact blood glucose control or increase cardiovascular risks.
Safe Choices:
- Copper IUD – hormone-free and won’t affect blood sugar
- Progestin-only pill – lower cardiovascular risk
- Hormonal IUD – localized hormone action, minimal effect on glucose
- Implant or Depo-Provera – may be safe under supervision
Be cautious: Estrogen-based birth control may elevate blood sugar or increase clot risk. Always consult your endocrinologist or OB-GYN.
3. Birth Control for Migraine Sufferers
Migraines especially with aura are a major red flag for estrogen-containing birth control. Estrogen can constrict blood vessels, raising stroke risk.
Safer Choices:
- Progestin-only pill
- Hormonal or copper IUD
- Implant
- Barrier methods
Never use combined pills with aura migraines. Non-hormonal methods are safest.
4. Birth Control for Obesity
Obesity can reduce the effectiveness of certain methods and increase risks like blood clots. Estrogen-based options are not ideal in many cases.
Preferred Methods:
- IUDs (hormonal or copper) – unaffected by weight
- Implant – long-lasting, consistent dosing
- Sterilization – permanent, non-hormonal
- Progestin-only methods
Note: Some studies suggest the patch may be less effective in women over 198 pounds. Talk to your provider.
5. Birth Control and Blood Clot Risk (Thrombophilia, Factor V Leiden)
If you have a clotting disorder or family history of blood clots, stay far away from estrogen-based contraceptives. They can drastically increase clot risk.
Best Choices:
- Copper IUD
- Hormonal IUD
- Progestin-only pill
- Barrier methods
Inherited thrombophilia demands extreme caution. A hematologist may need to be involved in your contraceptive care plan.
6. Birth Control for PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
PCOS is one condition where hormonal birth control can offer benefits beyond contraception, such as:
- Regulating irregular periods
- Reducing acne
- Decreasing androgen levels
- Protecting against endometrial hyperplasia
Ideal Options:
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) – help balance hormones
- Hormonal IUD – reduces heavy bleeding and cramps
- Progestin-only options – for those with clot risk or obesity
Avoid: Non-hormonal options if the goal includes hormonal regulation. Always match treatment goals to contraceptive method.
7. Postpartum or Breastfeeding Mothers
Right after childbirth, estrogen-based birth control is generally not recommended due to clot risks and potential impact on milk supply.
Best Birth Control After Delivery:
- Progestin-only pill – safe while nursing
- IUDs (inserted 6 weeks postpartum)
- Implant
- Barrier methods
Estrogen-based pills can reduce milk production wait at least 6 weeks postpartum or until you’ve stopped breastfeeding.
Side Effects and Risks You Should Know
Choosing a birth control method isn’t just about how well it prevents pregnancy. It’s also about how it affects your body, mind, and long-term health. Even the best birth control options in USA come with potential side effects some mild, some more serious. Knowing what to expect helps you make a confident, informed decision tailored to your body.
Let’s dive into the possible side effects, risks, and what they really mean for your health.
Common Side Effects of Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal contraceptives (like the pill, patch, ring, injection, IUD, and implant) work by adjusting your body’s natural hormone levels. This can lead to temporary changes most mild and manageable but occasionally significant for some users.
1. Irregular Bleeding or Spotting
- Especially common during the first 3 months
- Often resolves with continued use
- More common with progestin-only methods
2. Nausea and Breast Tenderness
- Common with estrogen-based methods (pill, patch, ring)
- Usually fades within a few weeks
- Taking pills with food may reduce nausea
3. Mood Changes and Depression
- Some users report mood swings, anxiety, or depression
- May be due to hormonal shifts affecting brain chemistry
- Switching to a different formulation or non-hormonal method can help
4. Weight Gain or Bloating
- Mostly reported with Depo-Provera injection
- Minimal or no weight gain with IUDs, pill, or patch
- Lifestyle factors often play a bigger role than hormones
5. Decreased Libido
- A small percentage report reduced sex drive
- Reversible upon discontinuation
- Not common with copper IUD or barrier methods
Final Thoughts: Choosing What’s Best for You
Birth control is not one-size-fits-all and that’s exactly what makes the decision both empowering and complex. The best birth control options in USA give you the freedom to take control of your reproductive health while aligning with your body, lifestyle, and long-term goals.
From hormonal options like pills, patches, and implants to non-hormonal choices like copper IUDs or barrier methods, every method has its own pros, cons, and potential side effects. And let’s not forget the long-acting solutions (LARCs) that offer low-maintenance convenience or permanent birth control for those who are done with family planning.
But here’s the truth: no method is perfect. What matters is what works best for you. That might mean prioritizing hormone-free alternatives, managing a health condition like PCOS, or choosing something discreet and long-lasting. Maybe you want the flexibility of condoms, or the confidence of an IUD. Either way, it’s your body and your choice.
Remember:
- Consult a healthcare provider who understands your medical history and preferences.
- Be open about your priorities whether that’s minimizing side effects, maximizing convenience, or balancing both.
- Don’t settle. If something feels off, speak up. You deserve a method that fits your life not the other way around.
In today’s world, you have options. Powerful, proven, and personalized ones.
So whether you’re starting birth control for the first time, switching after years, or just gathering information know this: you’re making a proactive decision about your health. That’s something to feel proud of.
Take your time. Ask the right questions. And choose what’s right for you not what someone else says is “best.”